Under BNSS, 2023 (India)
1. Commission of Offence
An offence is committed which is punishable under law.
Example:
A woman alleges that she was cheated and physically exploited on the false promise of marriage.
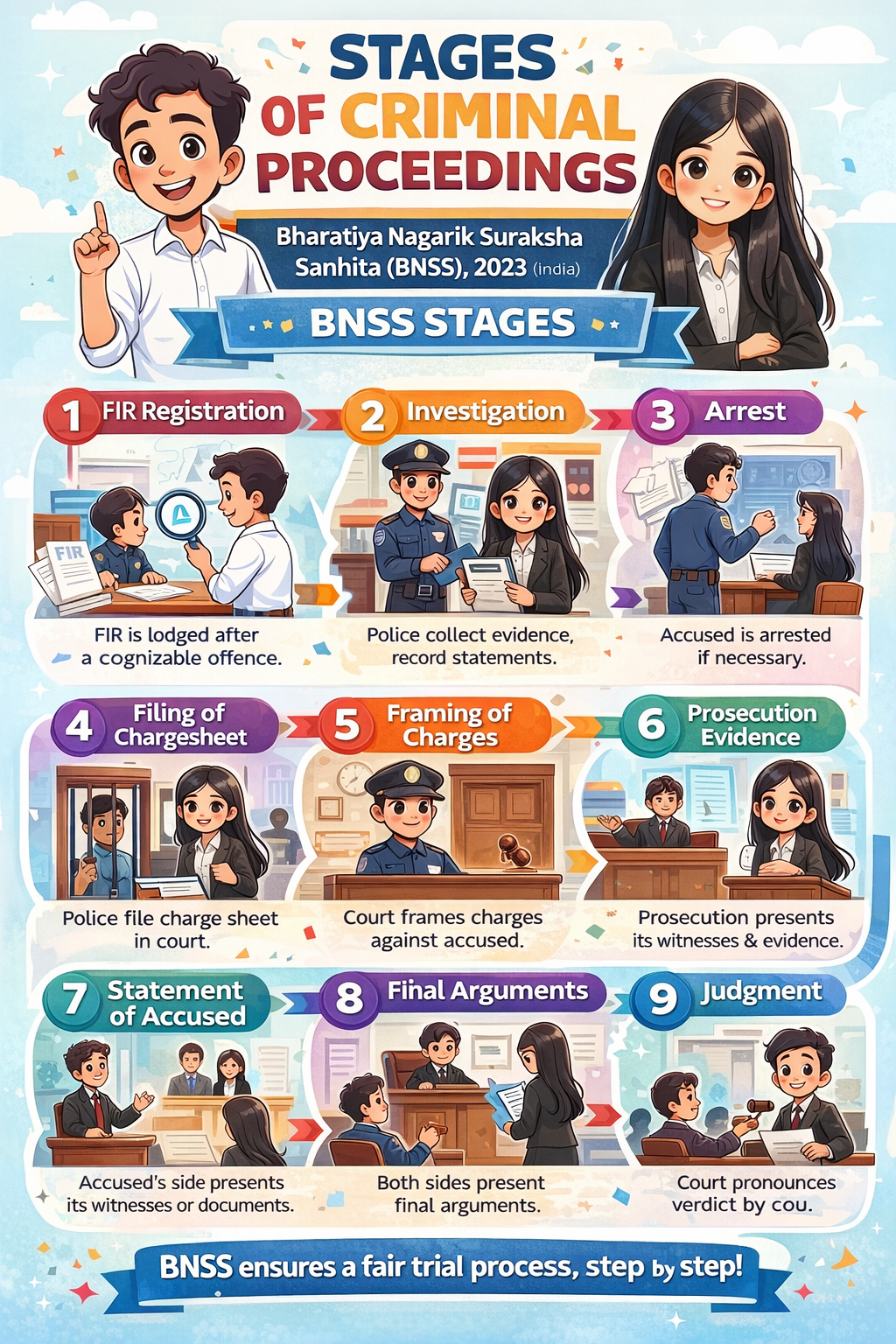
2. Information to Police (FIR)
Section 173 BNSS (equivalent to old Section 154 CrPC)
- Information relating to a cognizable offence is given to police
- FIR is registered
Example:
The woman lodges an FIR at the police station alleging offence under Section 69 BNS.
3. Investigation by Police
Sections 174–193 BNSS
Includes:
- Visit to place of occurrence
- Recording statements
- Collection of documents / electronic evidence
- Medical examination (if required)
Example:
Police seize mobile phones, collect WhatsApp chats, record statements of witnesses.
4. Arrest of Accused (if required)
Sections 35–62 BNSS
- Arrest may be made with or without warrant
- Grounds of arrest must be informed
- Arrest memo mandatory
Example:
Accused is arrested after preliminary investigation.
5. Production before Magistrate
Section 58 BNSS
- Accused must be produced before Magistrate within 24 hours
- Magistrate decides police custody / judicial custody
Example:
Accused is produced before Magistrate and sent to judicial custody.
6. Bail Stage
Sections 478–489 BNSS
- Bail may be granted depending on nature of offence
- Regular bail / interim bail / anticipatory bail
Example:
Accused applies for regular bail before Sessions Court.
7. Filing of Police Report (Charge Sheet)
Section 193 BNSS
(Equivalent to Section 173 CrPC)
- Police file final report before court
- Either charge sheet or closure report
Example:
Police file charge sheet alleging offence under Section 69 BNS.
8. Cognizance by Court
Section 210 BNSS
- Court takes cognizance of offence
- Case formally instituted
Example:
Sessions Court takes cognizance of offence.
9. Supply of Documents to Accused
Section 230 BNSS
- FIR, statements, documents supplied to accused
Example:
Accused receives copy of FIR, statements, electronic evidence.
10. Framing of Charge
Sections 250–252 BNSS
- Court decides whether sufficient ground exists to proceed
- Charge is framed or accused discharged
Example:
Court frames charge under Section 69 BNS.
11. Prosecution Evidence (PE)
Sections 254–263 BNSS
- Examination of prosecution witnesses
- Cross-examination by defence
Example:
Prosecutrix and IO are examined and cross-examined.
12. Statement of Accused
Section 266 BNSS
(Equivalent to Section 313 CrPC)
- Accused is questioned on evidence against him
- No oath required
Example:
Accused denies allegations and claims consensual relationship.
13. Defence Evidence (Optional)
Section 267 BNSS
- Accused may lead defence evidence
Example:
Accused produces WhatsApp chats and defence witnesses.
14. Final Arguments
- Oral and written submissions by both sides
Example:
Defence argues that relationship was consensual and no offence is made out.
15. Judgment
Section 271 BNSS
- Court delivers judgment
- Conviction or acquittal
Example:
Court acquits accused holding that offence is not proved beyond reasonable doubt.
16. Sentence (If Convicted)
Section 272 BNSS
- Hearing on sentence
- Punishment awarded
17. Appeal / Revision
Sections 413–455 BNSS
- Appeal before higher court
- Revision if applicable
ONE-LINE SUMMARY
BNSS criminal proceedings move from offence → FIR → investigation → trial → judgment → appeal, ensuring fairness to both victim and accused.
CrPC vs BNSS (2023)
Stage-wise Comparison + Practical Trial Strategy
I️⃣ CrPC vs BNSS — STAGE-WISE COMPARISON TABLE
| Stage | CrPC, 1973 | BNSS, 2023 | Practical Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIR | S.154 | S.173 | Zero FIR, digital FIR strengthened |
| Preliminary Enquiry | Judicially evolved | S.173(3) | Mandatory in certain offences |
| Investigation | S.156–173 | S.174–193 | Timelines introduced |
| Arrest | S.41–60A | S.35–62 | Arrest memo + rights emphasized |
| Production before Magistrate | S.57 | S.58 | Same principle |
| Remand | S.167 | S.187 | Judicial custody rules clarified |
| Bail | S.436–439 | S.478–489 | Victim hearing mandatory |
| Charge Sheet | S.173 | S.193 | Time-bound filing |
| Cognizance | S.190 | S.210 | Same concept |
| Supply of Documents | S.207 | S.230 | Includes digital records |
| Framing of Charge | S.228 | S.250–252 | Discharge strengthened |
| Prosecution Evidence | S.231 | S.254–263 | Witness protection focus |
| Statement of Accused | S.313 | S.266 | Same, renamed |
| Defence Evidence | S.233 | S.267 | Accused rights clearer |
| Arguments | Practice based | Practice based | Written arguments encouraged |
| Judgment | S.235 | S.271 | Time-bound pronouncement |
| Sentence | S.235(2) | S.272 | Victim impact hearing |
| Appeal | S.372–394 | S.413–455 | Victim appeal rights expanded |
II️⃣ BNSS – STAGE-WISE SECTIONS (FOR EXAM / COURT NOTES)
Pre-Trial Stage
- FIR – S.173
- Investigation – S.174–193
- Arrest – S.35–62
- Remand – S.187
- Bail – S.478–489
Trial Stage
- Cognizance – S.210
- Supply of documents – S.230
- Charge / Discharge – S.250–252
- Prosecution Evidence – S.254–263
- Statement of Accused – S.266
- Defence Evidence – S.267
- Arguments – (Court practice)
- Judgment – S.271
- Sentence – S.272
Post-Trial
- Appeal – S.413–455
- Revision – S.457 onwards
III️⃣ REAL TRIAL STRATEGY — STAGE-WISE (DEFENCE-ORIENTED)
1. FIR Stage (S.173 BNSS)
Strategy
- Check delay, jurisdiction, contradictions
- Apply for quashing / discharge groundwork
- Preserve electronic defence evidence early
2. Investigation Stage (S.174–193)
Strategy
- Challenge illegal arrest
- Seek seizure memo, CDRs, CCTV
- File representation to IO for fair investigation
3. Bail Stage (S.478–489)
Strategy
- Highlight lack of custodial interrogation
- Use medical, CDR, chats
- Argue proportionality + liberty
4. Charge Sheet Stage (S.193)
Strategy
- Scrutinize:
- Missing sanction
- Defective 65B certificate
- Interested witnesses
- Prepare discharge application
5. Framing of Charge (S.250–252)
MOST CRUCIAL STAGE
- Argue:
- Ingredients not made out
- Civil / consensual nature
- Cite Supreme Court / HC judgments
6. Prosecution Evidence (S.254–263)
Cross-Examination Strategy
- Contradictions (S.161 vs testimony)
- Delay, conduct, improbabilities
- Electronic evidence authenticity
7. Statement of Accused (S.266)
Strategy
- Short, consistent, denial
- Do NOT fill prosecution gaps
- Prepare answers in advance
8. Defence Evidence (S.267)
Optional but Powerful
- Produce:
- Chats, photos, call logs
- Neutral witnesses
- File proper 65B certificate
9. Final Arguments
Winning Formula
- Ingredients test
- Benefit of doubt
- Conduct of prosecutrix
- Case-law mapping
10. Judgment (S.271)
Focus
- Non-proof beyond reasonable doubt
- Acquittal precedents
Our Linkedin
https://www.linkedin.com/in/ushavats/



Add a Comment